The Emerging LLM Stack: A New Paradigm in Tech Architecture
As seasoned developers, we've witnessed the ebb and flow of numerous tech stacks. From the meteoric rise of MERN to the gradual decline of AngularJS, and the innovative emergence of Jamstack, tech stacks have been the backbone of web development evolution.
Enter the LLM Stack - a cutting-edge tech stack designed to revolutionize how developers build and scale LLM (Large Language Model) applications.
Why a New Stack for LLM Applications?
LLM applications are deceptively simple to kickstart, but scaling them unveils a Pandora's box of challenges:
- Platform Limitations: Traditional stacks struggle with the unique demands of LLM apps.
- Tooling Gaps: Existing tools often fall short in managing LLM-specific workflows.
- Observability Hurdles: Monitoring LLM performance requires specialized solutions.
- Security Concerns: LLMs introduce new vectors for data breaches and prompt injections.
To illustrate this evolution, we've created a companion blog that walks through a real-world LLM application's journey from MVP to scalable product.
Anatomy of the LLM Stack
Let's dissect the architecture of a robust LLM stack, based on our detailed example:
Please note that this article is not going to tell you what stack to choose, but rather outlines the components for building an LLM stack.
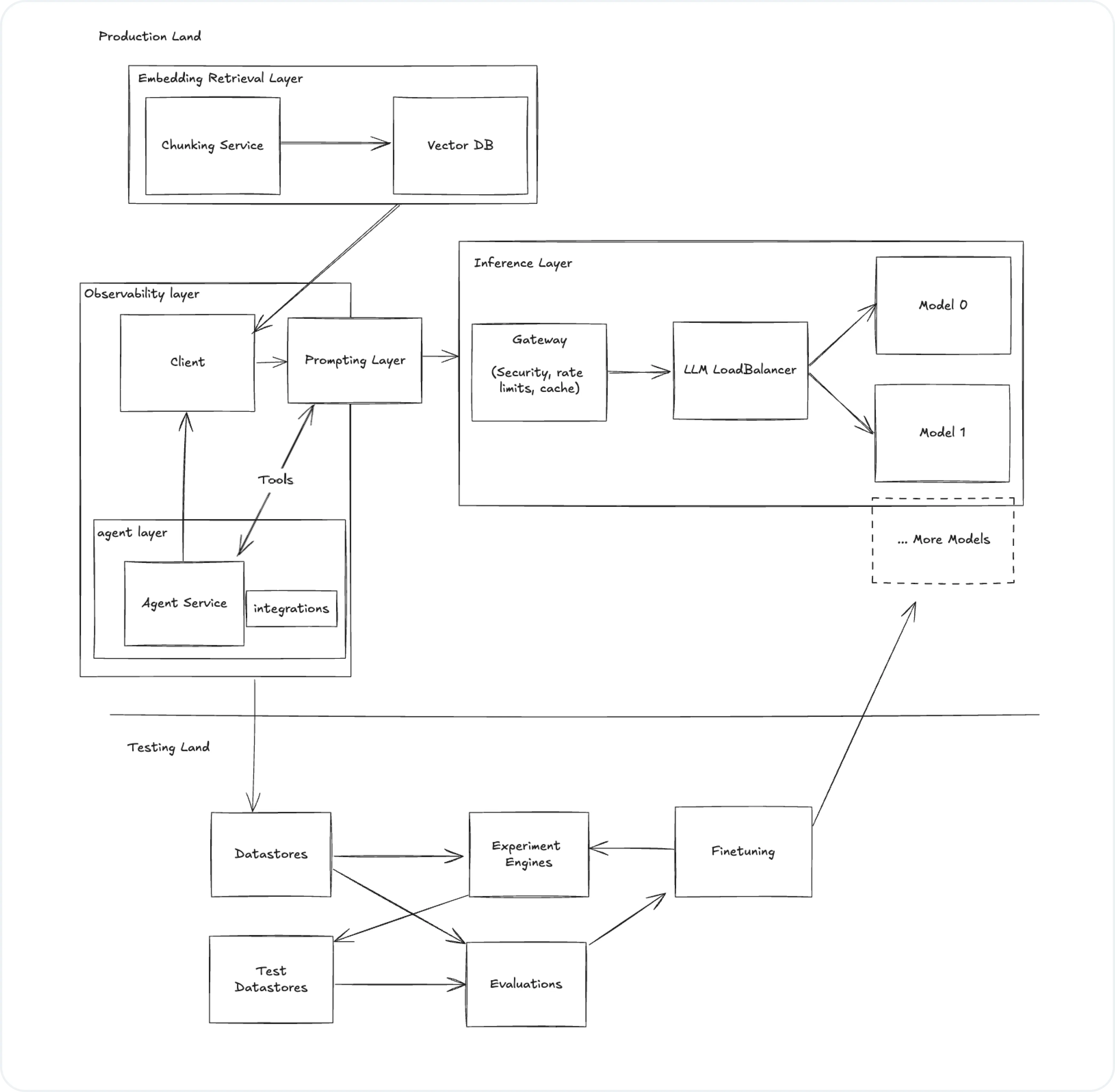
Key Components
1. Observability Layer
This layer focuses on monitoring, tracking, and analyzing the performance and behavior of LLM applications. It provides insights into how the models are being used, their performance metrics, and helps in debugging and optimizing the system.
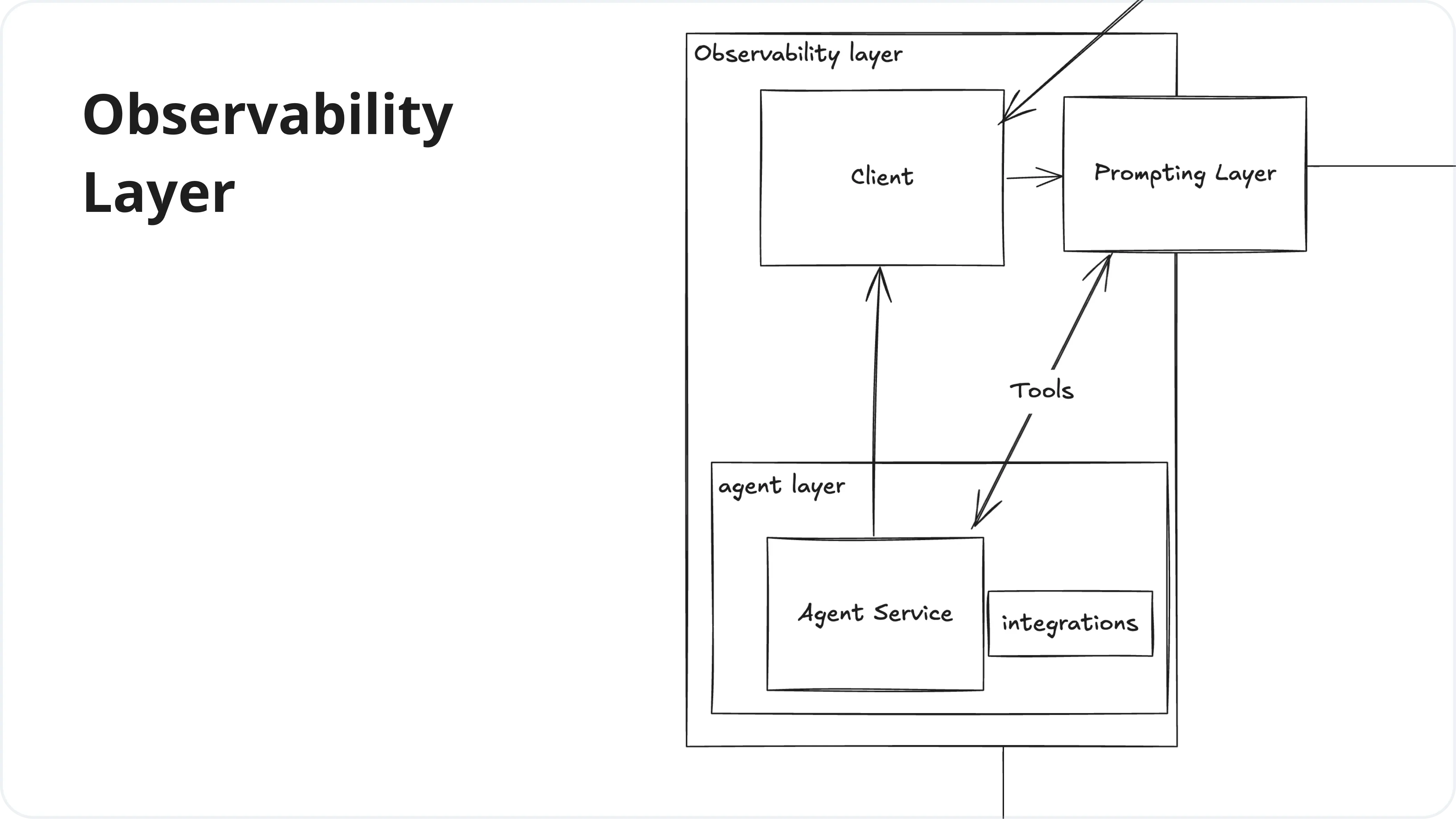
| Service | Cutting-Edge Solutions |
|---|---|
| Observability | Helicone, LangSmith, LangFuse, Traceloop, PromptLayer, HoneyHive, AgentOps |
| Clients | LangChain, LiteLLM, LlamaIndex |
| Agents | CrewAI, AutoGPT, DifyAI, Autogen |
| Prompting Layer | Helicone Prompting, PromptLayer, PromptFoo |
| Integrations | Zapier, LlamaIndex |
You might be interested:
-
Comparing the Best Observability Tools for LLM Applications
-
6 Awesome Platforms & Frameworks for Building AI Agents
2. Inference Layer
The Inference Layer is responsible for processing requests to the LLM, managing model deployments, and load balancing. It handles the actual execution of the language models and ensures efficient and scalable access to these models.
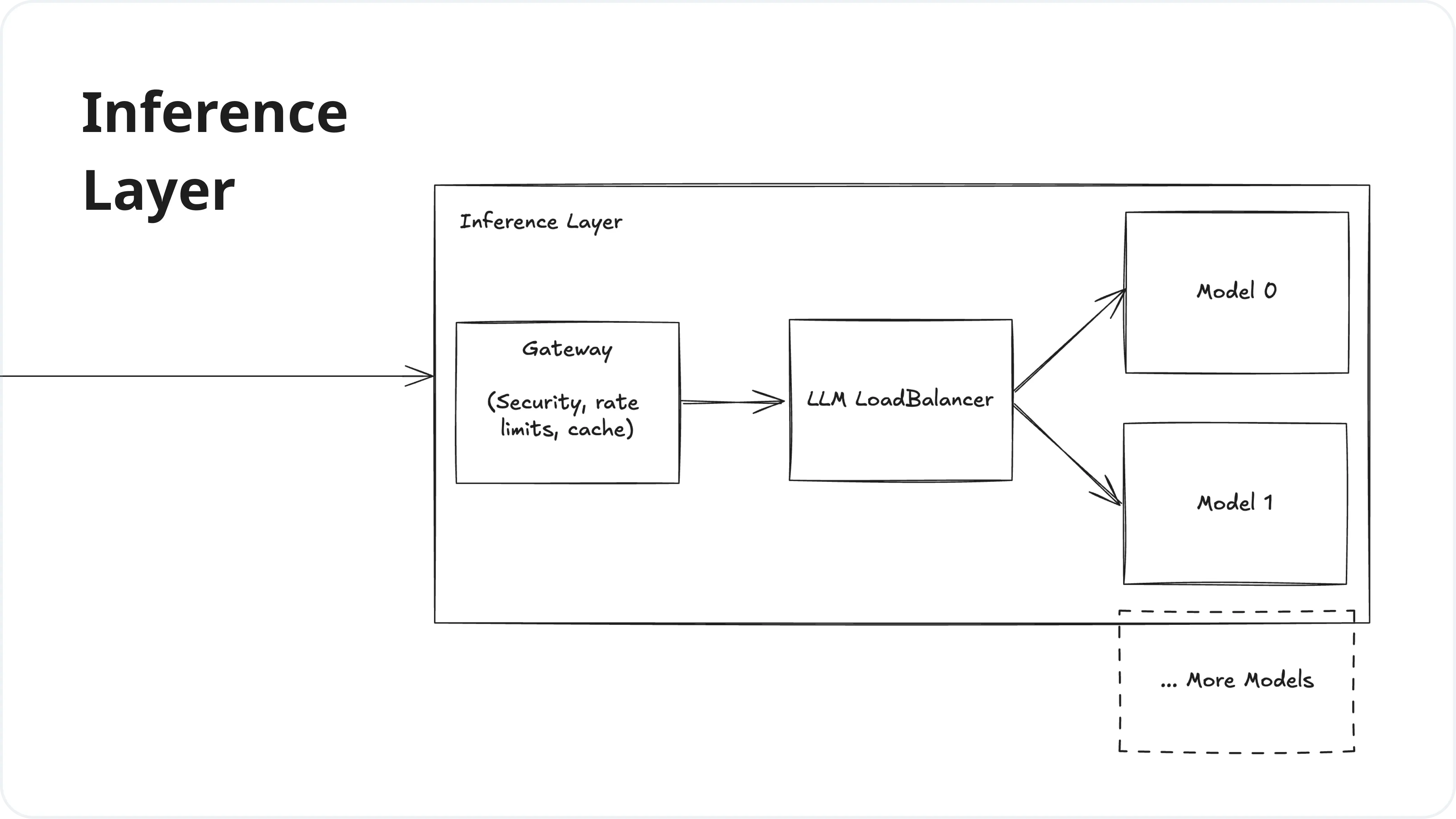
| Service | Innovative Products |
|---|---|
| Gateway | Helicone Gateway, Cloudflare AI, PortKey, KeywordsAI |
| LLM Load Balancer | Martian, LiteLLM |
| Model Providers | OpenAI (GPT), Meta (Llama), Google (Gemini), Mistral, Anthropic (Claude), TogetherAI, Anyscale, Groq, Amazon (Bedrock) |
You might be interested: Top 10 AI Inference Platforms in 2025
3. Testing & Experimentation Layer
This layer enables developers to test, evaluate, and experiment with different prompts, models, and configurations. It provides tools for fine-tuning models, running experiments, and assessing the quality and performance of LLM outputs.
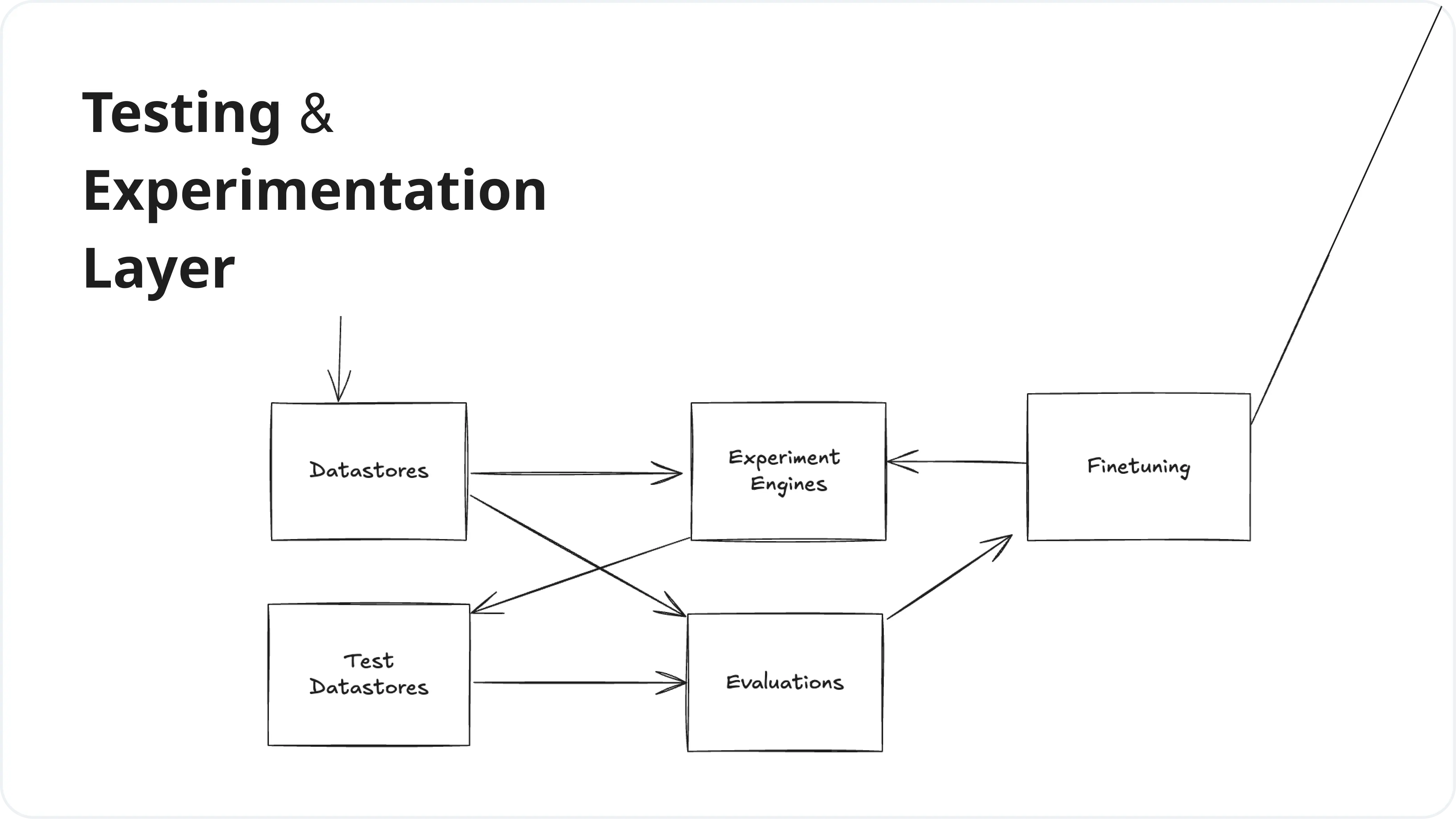
| Service | Next-Gen Tools |
|---|---|
| Datastores | Helicone API, LangFuse, LangSmith |
| Experimentation | Helicone Experiments, Promptfoo, Braintrust |
| Evaluators | PromptFoo, Lastmile, BaseRun |
| Fine Tuning | OpenPipe, Autonomi |
Helicone: Developer's LLM Toolkit
Helicone provides two core components that developers need when building production LLM apps: a Gateway for managing traffic and an Observability layer for monitoring and debugging. Think of it like having both a load balancer and logging/monitoring system purpose-built for LLMs to help you build more robust and scalable applications.
![]()
By integrating Helicone into your LLM workflow, you're not just adopting a tool; you're embracing a philosophy of efficiency, scalability, and deep insights into your LLM applications.
Ready to supercharge your LLM development? Dive deeper into Helicone's capabilities and see how it can transform your LLM stack today!
Further Resources
-
LLM Architecture From Simple Chatbot to Complex System
-
4 Essential Helicone Features to Optimize Your LLM App
-
Building Your First AI App with Helicone
Questions or feedback?
Are the information out of date? Please raise an issue or contact us, we'd love to hear from you!